Imagine a dinner in the Banquet Hall with George and Edith Vanderbilt. Your place at the 40-foot-long table might be set with as many as twelve pieces of silverware, three plates, plus a charger as well as cup and saucer made by made by British porcelain manufacturers Minton or Spode-Copeland. Baccarat crystal wine, sherry, and water glasses are set within your reach.
Meals at Biltmore were prepared with the utmost care and that attention to detail extended to the whole dining experience. In George Vanderbilt’s papers, Biltmore archivists found record of a purchase of monogrammed linen napkins from a shop in Paris, dated September 24, 1895. Details such as linens played a big role in the Vanderbilts’ spirit of gracious hospitality, but keeping these delicate items clean, crisp, and perfect required efforts almost unimaginable today.
In her 1903 book, Millionaire Households and Their Domestic Economy: Hints for Fine Living, Mary Elizabeth Carter− former housekeeper to another branch of the Vanderbilt family− gave a behind-the-scenes look at how houses such as Biltmore handled the excess laundry created by guests. “If you’re not prepared for large entertainment,” she warned, “bedlam is let loose below stairs and laundresses are driven almost mad.”
In Carter’s view, a well furnished laundry was essential to cope with the demands of a house designed for entertainment:
“The twentieth century laundry is supplied with a diversity of smoothing irons – heavy ones for house linens, medium weight for lingerie and little ones of various and curious shapes for smoothing out sleeves and to reach tiny places in the smallest and most fairy-like of baby clothes. Its ventilation is perfect and the water supply, both hot and cold, is perfect.…A spacious, sunlighted (sic) finely ventilated laundry amply furnished for the work to be accomplished in the best manner for the workers speaks eloquently for the character of the ruling classes.”
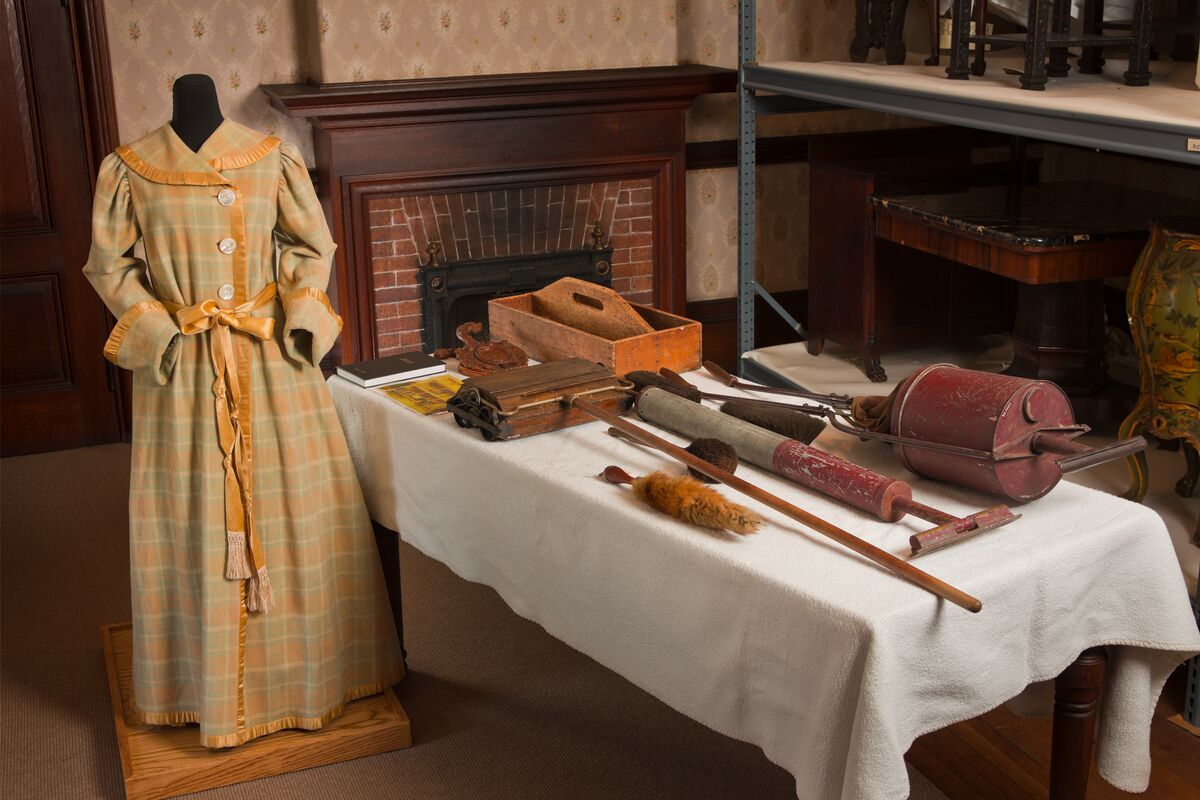
In the Main Laundry and Drying Room at Biltmore, you’ll see a variety of pressing devices as well as a barrel washer operated with leather belts and pulleys and an extractor used to spin excess moisture from laundry. The “ironing mangle” was used to iron large, flat articles such as linens and the innovative system of rolling, wooden racks were used for drying, either by air or electric coils.
Carter went on to say of homes such as Biltmore that “None but skilled hands find employment in the laundry of one of these houses. They handle countless expensive and delicate articles of wearing apparel and house linen and must send all back looking as beautiful as if it had just arrived from Paris.”
As you tour Biltmore House keep an eye out for the little details such as the linens, each of which adds to the sense of being in a place where guests receive an extraordinary welcome.
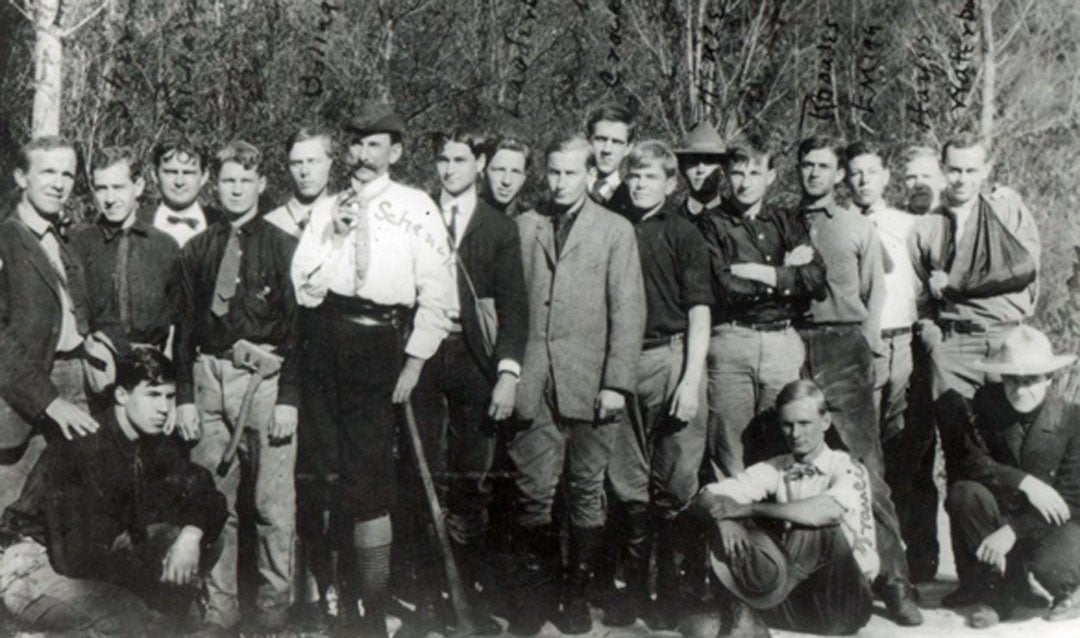
















 Mrs. Vanderbilt planned to employ Patrick “to take charge of her garden and grounds around her new home” once his condition improved. Patrick wrote to Mrs. Vanderbilt:
Mrs. Vanderbilt planned to employ Patrick “to take charge of her garden and grounds around her new home” once his condition improved. Patrick wrote to Mrs. Vanderbilt:




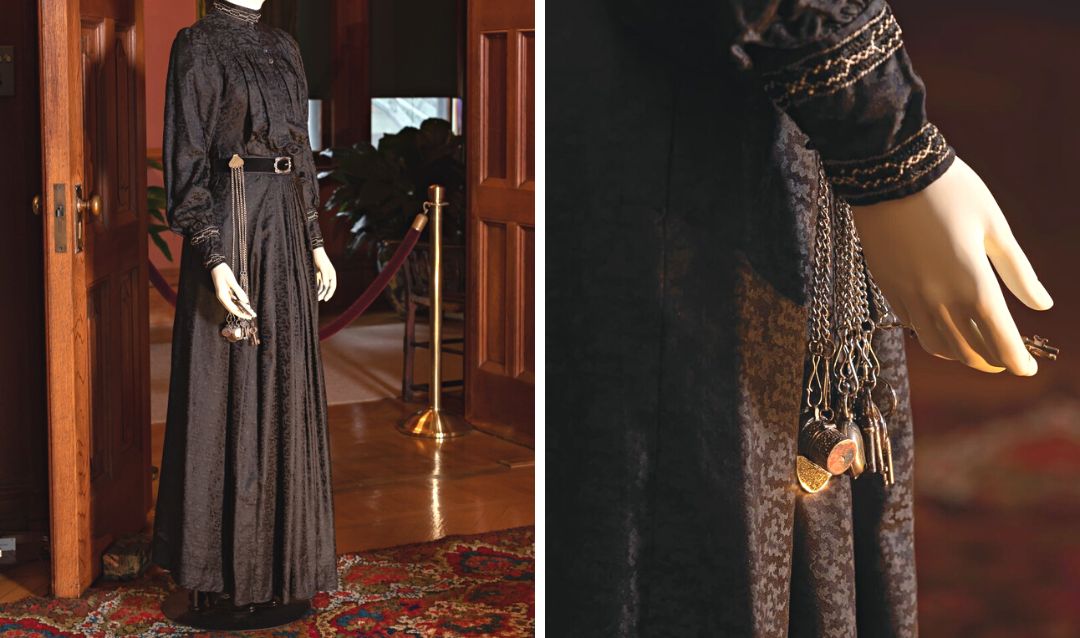
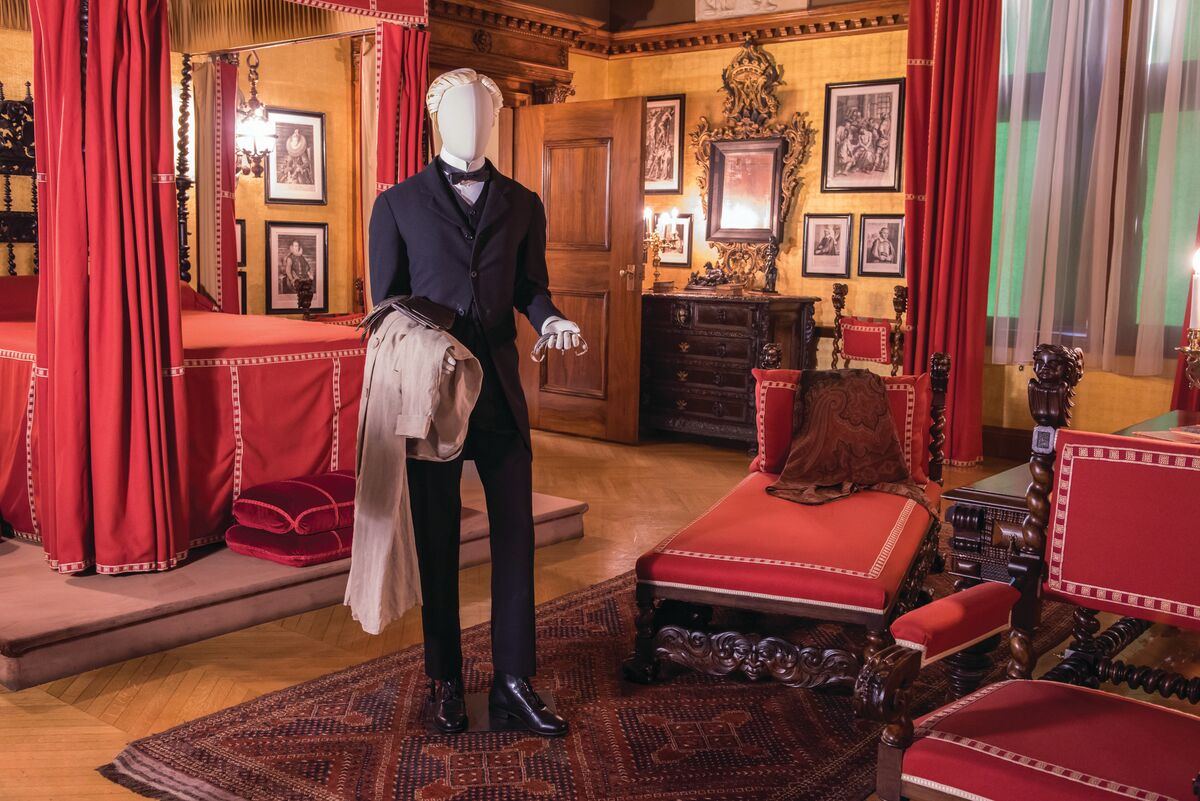
 (Right) Standing portrait
(Right) Standing portrait

